We first draw an empty frame with the axes, then draw the graphs on top of it Note that the graphs should have the same or very close ranges (in both axis), otherwise they may not be visible in the frame.
import numpy as np
import ROOT
c1 =
ROOT.TCanvas(
"c1",
"2 graphs with errors", 200, 10, 700, 500)
n1 = 10
xval1 =
np.array([-0.22, 0.05, 0.25, 0.35, 0.5, 0.61, 0.7, 0.85, 0.89, 0.95])
yval1 =
np.array([1, 2.9, 5.6, 7.4, 9, 9.6, 8.7, 6.3, 4.5, 1])
ex1 =
np.array([0.05, 0.1, 0.07, 0.07, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.05])
ey1 =
np.array([0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8])
n2 = 10
xval2 =
np.array([-0.28, 0.005, 0.19, 0.29, 0.45, 0.56, 0.65, 0.80, 0.90, 1.01])
yval2 =
np.array([0.82, 3.86, 7, 9, 10, 10.55, 9.64, 7.26, 5.42, 2])
ex2 =
np.array([0.04, 0.12, 0.08, 0.06, 0.05, 0.04, 0.07, 0.06, 0.08, 0.04])
ey2 =
np.array([0.6, 0.8, 0.7, 0.4, 0.3, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7])
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.


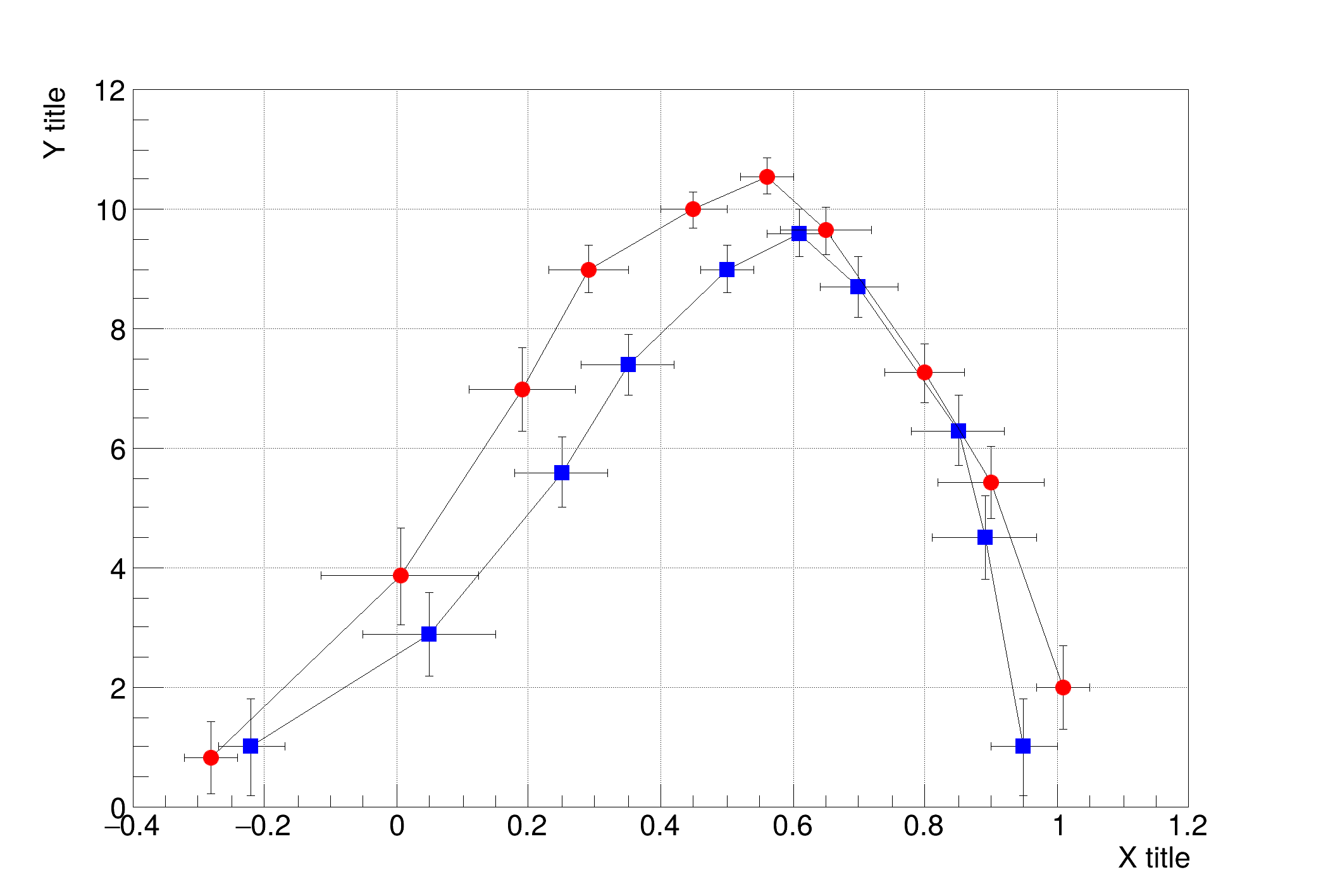 Create and draw two graphs with error bars, superposed on the same canvas
Create and draw two graphs with error bars, superposed on the same canvas 