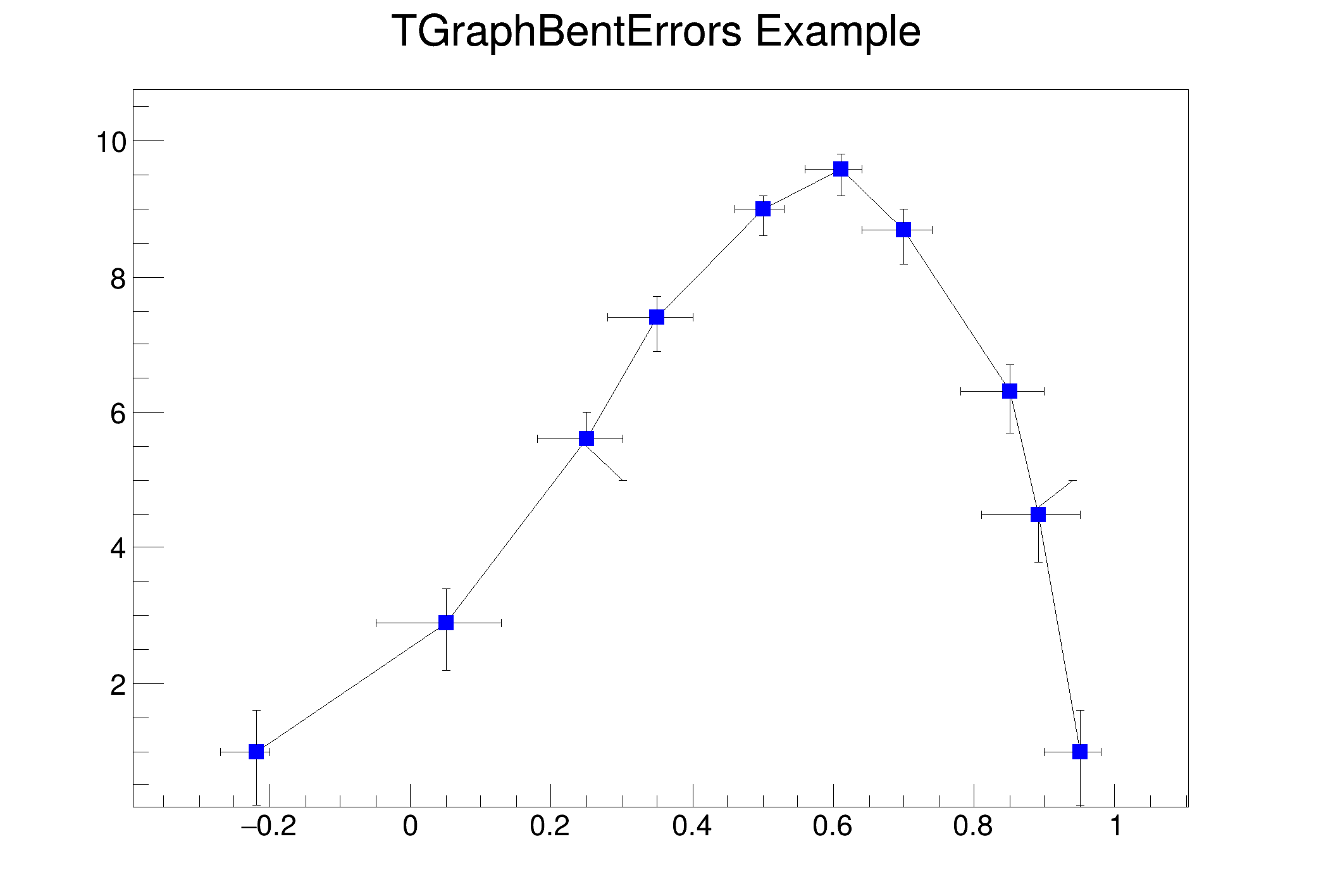
Inspired from work of Olivier Couet.
exl / exh: low and high (left/right) errors in x; similar for y e*d: delta, in axis units, to be added/subtracted (if >0 or <0) in x or y from the data point's position to use as end point of the corresponding error
import ROOT
n = 10
for i in [-0.22, 0.05, 0.25, 0.35, 0.5, 0.61, 0.7, 0.85, 0.89, 0.95]:
for i in [1, 2.9, 5.6, 7.4, 9, 9.6, 8.7, 6.3, 4.5, 1]:
for i in [0.05, 0.1, 0.07, 0.07, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.07, 0.08, 0.05]:
for i in [0.8, 0.7, 0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6, 0.7, 0.8]:
for i in [0.02, 0.08, 0.05, 0.05, 0.03, 0.03, 0.04, 0.05, 0.06, 0.03]:
for i in [0.6, 0.5, 0.4, 0.3, 0.2, 0.2, 0.3, 0.4, 0.5, 0.6]:
for i in [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]:
for i in [0.0, 0.0, 0.05, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]:
for i in [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0]:
for i in [0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.0, 0.05, 0.0]:
n,
)
ROOT::Detail::TRangeCast< T, true > TRangeDynCast
TRangeDynCast is an adapter class that allows the typed iteration through a TCollection.